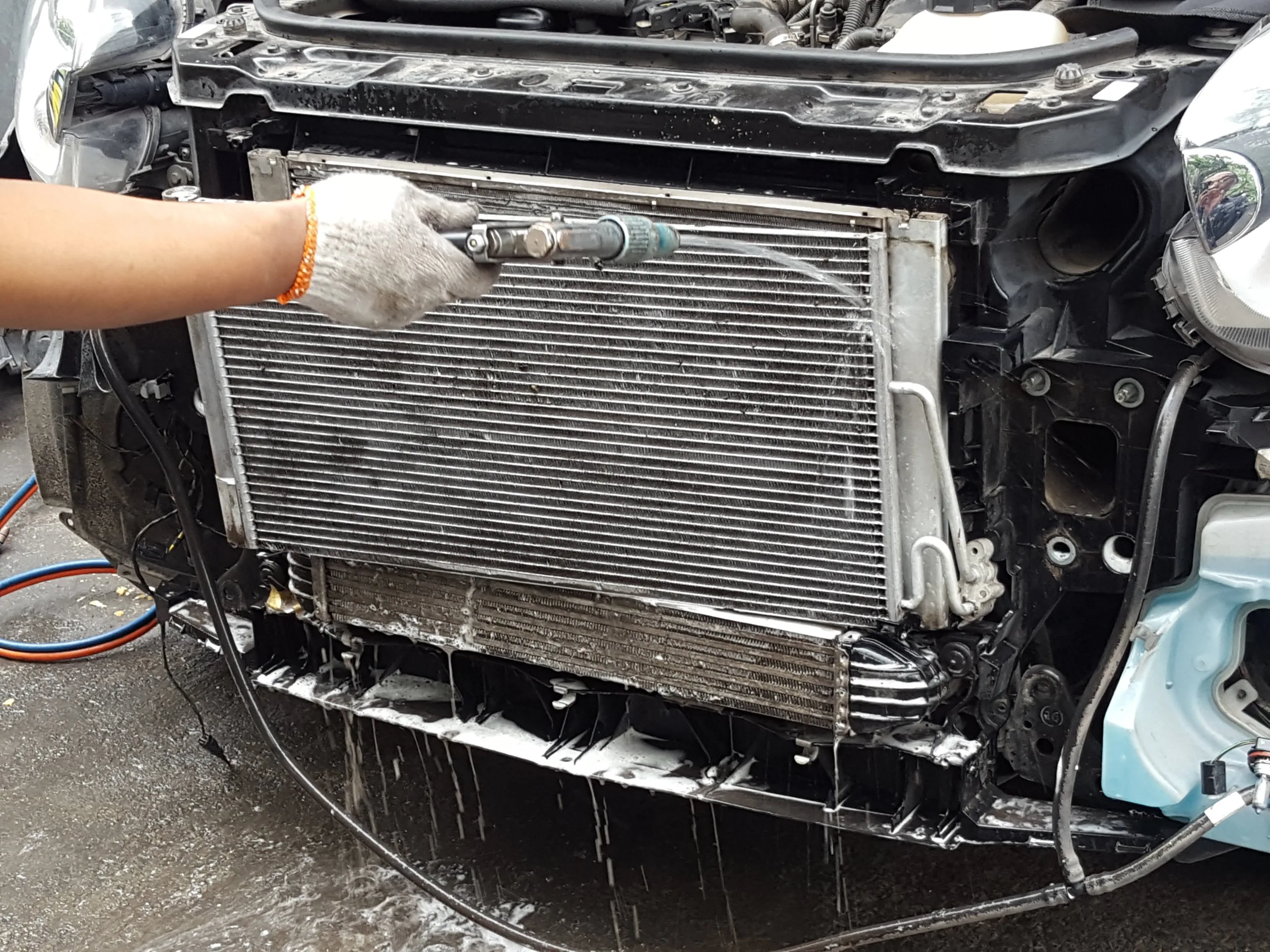
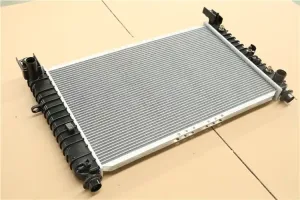
As the core component of the engine cooling system, the radiator is essential for the normal operation of the engine. Its function is to dissipate the heat of the engine into the air to ensure that the engine remains within the appropriate temperature range.
Once the radiator fails, the coolant (antifreeze) temperature will be too high, causing the engine to overheat, which is very harmful.
What factors will cause the premature failure of the radiator? To understand this problem, we need to first understand the working principle of the radiator.
1. Working principle of radiator
The radiator is a heat exchanger whose main task is to dissipate the heat absorbed by the engine coolant to the outside air. Its working process is as follows.
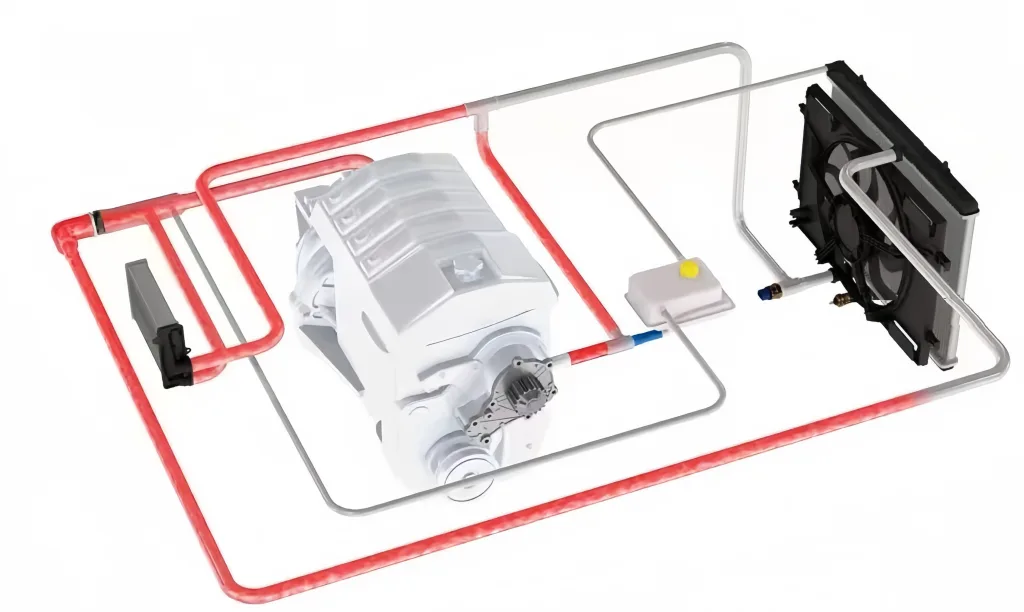
(1) Coolant carries heat
As the coolant flows in the engine cooling lines, it absorbs heat from the engine. The water pump in the cooling system pumps the high-temperature coolant from the engine to the radiator.
(2) Heat exchange
The coolant enters the radiator’s tiny pipes, which are surrounded by many metal fins. The fins are designed to help dissipate heat. At the same time, the car’s fan or airflow during driving helps accelerate the heat dissipation of these fins, so that the heat in the coolant is dissipated to the outside air.
(3) Cooling
Through this heat exchange process, the coolant temperature drops and then returns to the engine, continuing to carry the engine’s heat to keep the engine at a suitable operating temperature, and the cycle repeats itself.

2. The main reasons for radiator failure
(1) Corrosion and clogging
Impurities and corrosion in the coolant may accumulate in the radiator, causing pipe blockage or blade damage. This reduces the efficiency of heat transfer and eventually causes the engine to overheat.
(2) Physical damage
A vehicle collision, stone hit or other physical damage while driving at high speed may cause the radiator to break and leak, resulting in coolant loss. If the amount of coolant is too little, it will cause high water temperature problems.

(3) aging
Over time, the radiator material will age, and the pipes or fins will deform and become damaged, resulting in reduced heat dissipation efficiency and causing cooling system failure.
(4) Neglect of maintenance
Regular replacement of coolant is an important item in cooling system maintenance. In addition to cooling and antifreeze, coolant also has an important function of anti-corrosion, effectively protecting the radiator and cooling system pipes. Therefore, if it is not replaced for a long time, the antifreeze will gradually become ineffective, lose its antifreeze and anti-corrosion effects, and cause radiator failure. In addition, for radiators with a long mileage, cleaning the radiator pipes when replacing the coolant will help improve the heat dissipation efficiency and extend the service life of the radiator.
3. Conclusion
The radiator plays a key role in the cooling system, and its regular maintenance should not be neglected. In addition to physical damage, the main factors causing premature failure of the radiator are internal corrosion and blockage. The coolant is responsible for the task of radiator corrosion prevention, and regular replacement can effectively prevent corrosion and blockage problems.
In addition, it should be noted that coolant deterioration (not replaced for a long time), use of inferior coolant or adding tap water can easily cause corrosion and clogging problems and should be avoided.